Maldives
Results in this brief are from an analysis of the 2009 Demographic and Health Survey. Information on methodology is in the main text of the report and in the method briefs. Additional results are available in Results Tables on the DDI website.
Share of Adults with Functional Difficulties
In the Maldives, the share of adults aged 15 and older with any functional difficulty stands at 24.7%. As shown in Table 1, it varies from a low of 19.1% in Male to a high of 33% in North Central. In all regions, seeing is the most common type of functional difficulty; communication and self-care are the least common.
Table 1: Maldives: Share of Adults with functional difficulties at the regional level (%)
| Region | Any | Seeing | Hearing | Mobility | Cognition | Self-Care | Communication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | 22.0 | 12.9 | 4.7 | 7.8 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 2.3 |
| Male | 19.1 | 10.6 | 2.9 | 7.8 | 4.5 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
| North | 28.0 | 16.5 | 5.6 | 11.9 | 7.9 | 2.7 | 3.0 |
| North Central | 33.0 | 21.1 | 6.7 | 12.7 | 11.3 | 2.1 | 3.0 |
| South | 25.4 | 17.6 | 5.0 | 8.8 | 5.9 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| South Central | 28.6 | 19.0 | 6.1 | 9.1 | 8.7 | 2.1 | 2.9 |
| National | 24.7 | 15.2 | 4.7 | 9.4 | 6.8 | 1.9 | 2.3 |
Notes: ‘Any’ is the share of adults with any level of difficulty (some difficulty, a lot of difficulty or unable to do in one or more functional domains. For instance, ‘Seeing’ is the share of adults with difficulty in seeing of any level. Shares for the six domains do not add up to the share of any difficulty as some individuals may have functional difficulties in more than one domain. Source: Own calculations based on Maldives DHS data.
Multidimensional Poverty
Multidimensional poverty captures an individual’s experience of multiple deprivations (e.g. low educational attainment, having inadequate living conditions). In the Maldives, the shares of persons with at least a lot of functional difficulty and some difficulty who are multidimensionally poor stands at 74.1% and 56.5%, respectively. This is higher than that of persons with no difficulty at 26.2%.
Thus, there is a disability gap in multidimensional poverty between persons with at least a lot of difficulty and no difficulty (47.9 percentage points) and between persons with some difficulty and no difficulty (30.3 percentage points). In other words, persons in the Maldives with functional difficulties more frequently experience multiple deprivations than those with no difficulties. As illustrated in Figure 1/Table 2, multidimensional poverty is common in all regions among adults with functional difficulties.
Figure 1: Maldives: Multidimensional poverty headcount among adults with no, some and at least a lot of difficulty (%)
Figure1a: Adults with no difficulty
Figure 1b: Adults with some difficulty
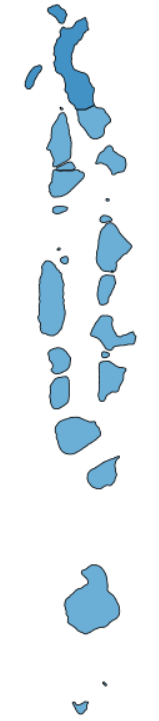
Figure 1c: Adults with at least a lot of difficulty
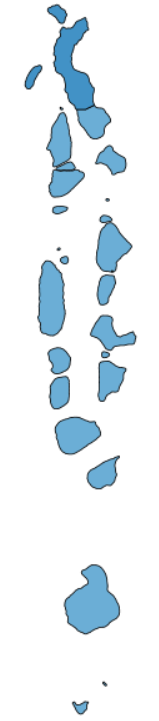
Source: Own calculations based on Maldives DHS data (2009). Central region is not shown. The notes of Table 1 apply. Each area represented in each map above may represent multiple islands.
Table 2 (supporting figure 1): Maldives: Multidimensional poverty headcount among adults with no, some and at least a lot of difficulty (%)
| Region | No difficulty | Some difficulty | At least a lot of difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central | 34.3 | 63.2 | 72.3 |
| Male | 14.4 | 35.1 | 59.1 |
| North | 33.2 | 70.4 | 82.7 |
| North Central | 31.5 | 65.7 | 77.6 |
| South | 33.0 | 60.9 | 75.7 |
| South Central | 35.5 | 67.3 | 81.5 |
| National | 26.2 | 56.5 | 74.1 |
 Go Back
Go Back