Health
Health is a multidimensional notion. This section tries to capture several aspects of health through nine indicators. The first two are indicators that are proxies for health and capture some of the living conditions of the household that are socio-economic determinants of health: the share of adults living in households with safely managed drinking water (CRPD Article 25, SDG indicator 6.1.1) and the share of adults living in households with safely managed sanitation (CRPD Article 25, SDG indicator 6.2.1). We also include the share of women who report having their family planning needs met through modern contraceptive methods (CRPD Article 23, SDG indicator 5.6.1).
While we do not have actual information on the experience of violence, we capture attitudes towards domestic violence with the share of women who think a husband is justified to hit his wife.12 In addition, we also present the share of women who report non-participation in activities due to menstruation and three different indicators related to HIV awareness and testing: the shares of women who (i) report having previously heard of HIV (awareness); (ii) correctly identify all three means of mother-to-child transmission of HIV; and, (iii) have ever been tested for HIV.
A. Result
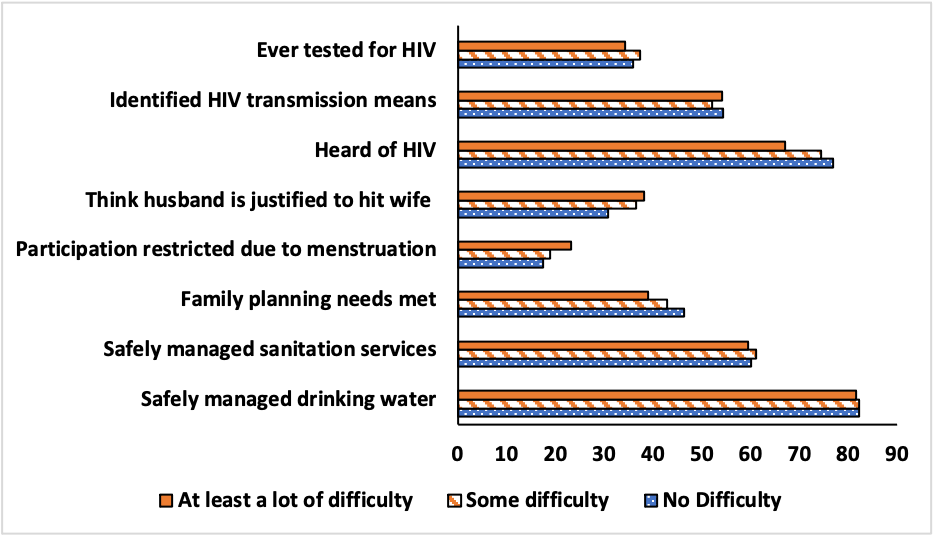
The entire set of results on health is available in the Health Results Tables (2022 results table ). Cross country estimates are shown in Figure 7.1 for all indicators.
For the share of adults with safely managed drinking water and the share with safely managed sanitation, cross-country estimates suggest that there is no significant difference among women by functional difficulty status. This holds for country-level estimates for most countries.
For the share of women who have their family planning needs met, cross-country estimates stand at 46.5%, 43% and 39% for women with no, some, and at least a lot of difficulty respectively. At the country level, a gap is found is under half of the countries under study.
In all the countries under study, the share of women who missed activities due to menstruation are at 18%, 20% and 23% for women with no, some, and at least a lot of difficulty respectively. A statistically significant difference across functional difficulty status is found in 21 out of 33 countries.
Figure 7.1: Cross-country estimates for health indicators among women (%)
Source: Authors’ calculations based on MICS6 data
Table 7.1 gives cross-country estimates for the share of women who think a husband is justified to hit his wife for the entire sample and subsamples. Overall, 30%, 35% and 37% of women with no difficulty, some difficulty, and at least a lot of difficulty respectively think that a husband is justified in hitting his wife. A significant difference across functional difficulty status is found in 25 out of 33 countries. Across functional difficulty status, the share of women who think a husband is justified to hit his wife tends to be larger among women age 30 to 44 compared to women age 18 to 29.
Finally, in cross country estimates, women with functional difficulties are found to be significantly less likely to have heard of HIV. For the other two indicators related to HIV (identify all three means of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and ever been tested), no difference is found in cross-country estimates and for most country-level estimates.
Table 7.1: Women who think husband is justified to hit wife (%)
| Sample | No Difficulty | Some difficulty | At least a lot of difficulty | Any difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All women | 30.7 | 36.6 | 38.3 | 36.9 |
| Rural | 35.0 | 41.8 | 42.9 | 41.6 |
| Urban | 26.9 | 32.3 | 33.9 | 31.6 |
| Age 18 to 29 | 32.2 | 37.3 | 40.3 | 37.0 |
| Age 30 to 49 | 32.2 | 38.3 | 39.3 | 37.1 |
| Seeing difficulties | – | – | – | 35.1 |
| Hearing difficulties | – | – | – | 39.0 |
| Walking difficulties | – | – | – | 38.8 |
| Cognitive difficulties | – | – | – | 39.1 |
| Selfcare difficulties | – | – | – | 36.9 |
| Communication difficulties | – | – | – | 45.0 |
Source: Authors’ calculations based on MICS6 data
Note: ‘-‘ refers to not applicable for ‘No difficulty’ and not available for ‘Some difficulty’ and ‘At least a lot of difficulty’ due to small sample sizes in many countries
B. Discussion
Results vary across health indicators. Unlike in the 2021 Report, we found no difference with respect to living in a household with safely managed water or sanitation for most countries. This may be due in part to the composition of our sample with some countries at higher levels of development that have safely managed water and sanitation for their entire population or close (e.g., Belarus).
Having a functional difficulty status is associated with higher rates of family planning needs not being met, missing activity due to menstruation, thinking a husband is justified to hit his wife, and not having heard of HIV. These results suggest that disability inclusion is needed in health services and in public health interventions.
SDG Target 3.7 aims for universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services, including for family planning, information, and education. SDG target 5.6 calls for access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights (United Nations 2019b). Our results suggest that work is needed for these targets to be achieved by 2030.
12 Hitting or beating his wife in relation to at least one of the following circumstances: (1) she goes out without telling him, (2) she neglects the children, (3) she argues with him, (4) she refuses sex with him, and (5) she burns the food.
 Go Back
Go Back